With many technological advancements and changes happening in the manufacturing industry, it can be hard to keep up. To put it simply, the future of manufacturing looks very promising. In fact, more than 670,000 manufacturing jobs have been added since 2021, according to Spectrum News. So, what does the future of productivity and growth in United States manufacturing look like? Let’s answer some looming questions about the manufacturing industry.
How Is Manufacturing Changing?
In recent decades, the United States seemed to be in danger of losing its position as a world-leading manufacturing economy. This can be contributed to design services and software activities rather than actual physical production. However, there are some recent trends that point to the potential for a growth resurgence.
Today, manufacturing in the United States is at its inflection point. For the decade leading up to the Covid-19 pandemic, many declines have recovered. In fact, 1.3 million manufacturing jobs were added to the economy between 2010 and 2019. This is record growth considering the loss of 5.8 million jobs over the previous 10 years. Because of this huge growth in the manufacturing industry, the United States’ global manufacturing gross domestic product (GDP), output, and exports stabilized.
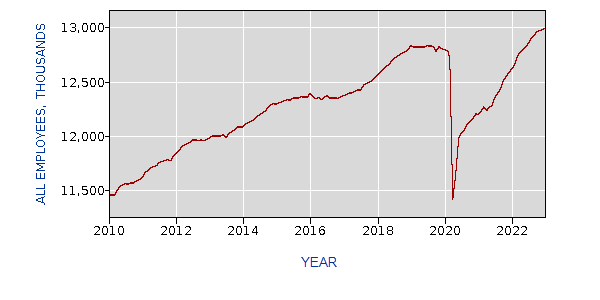
Accelerating this upturn could improve the resilience of the overall United States economy and have transformative effects both economically and socially. The McKinsey Global Institute predicts that resorting the growth and competitiveness in key manufacturing sectors could have incredible effects on our economy. In fact, they estimate boosting U.S. GDP by more than 15% for the rest of the decade until 2029.
What Happens to the Manufacturing Industry if There’s a Recession?
If you want to succeed in the manufacturing industry, you need to understand how the industry was affected in the last recession and what could happen if there’s another one. As mentioned previously, the manufacturing industry just started to recover between 2010 and 2019 from the last recession. Here are some reasons that have been contributed to the decline.
- Supply chain disruptions
- Rising trade with China
- Skills mismatch
- Decline in cross-regional migration
Of course, there are many other factors that have led to declines in the manufacturing industry. According to the 2018 Deloitte and the Manufacturing Institute skills gap and future of work study, there’s been a shift to a service-based economy. This includes financial and banking services as well as an increased demand in the healthcare sector. This shift combined with the higher standard of living in the United States nowadays have made labor costs much higher than other countries, which contributes directly to the decline of the manufacturing industry.
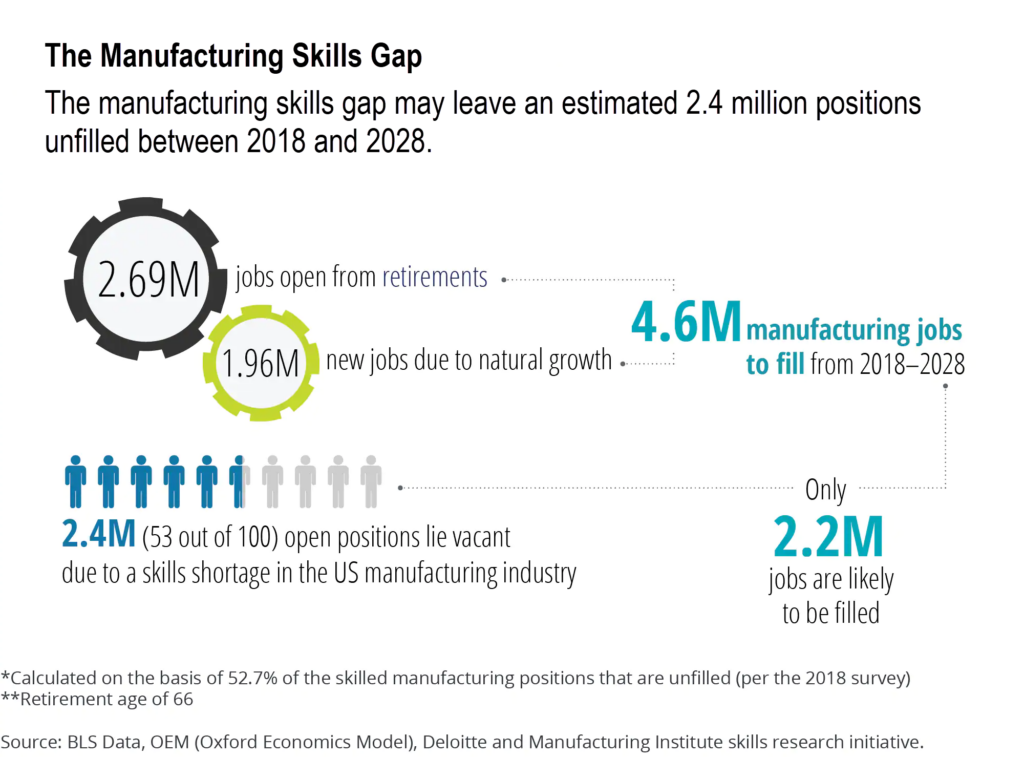
While all of the previously mentioned factors play a role in the manufacturing industry, skills mismatch and talent shortage continue to be a barrier for growth. Skills mismatch is when there is a gap between the skills workers have and the skills employers need. In fact, Deloitte reports that 80% of executives agree there is currently a talent shortage in the American manufacturing industry. Because of the talent shortage due to skill mismatch, 2.4 million jobs could be left unfilled, costing the industry nearly $455 billion by 2028.
What Effect Does the CHIPS and Science Act Have?
The Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors (CHIPS) and Science Act of 2022 has revitalized domestic manufacturing, strengthened American supply chains, and created well-paying American jobs. The CHIPS and Science Act, which was signed into law on August 9th, 2022, boosts American semiconductor research, development, and production. In turn, it helps ensure that the United States remains a leader in the technology that is the foundation for defense systems, household appliances, automobiles, and more.
While Americans invented the semiconductor, today we only produce about 10% of the world supply. In fact, 75% of global semiconductor production comes from East Asia. Luckily, the CHIPS and Science Act unlocked hundreds of billions for semiconductor investment across the country, including critical sectors and national defense. This law also ensures that the United States will maintain and advance its technological and scientific edge, ensuring the future is made in America and creating more opportunities in the science and technology sectors.
Here are some effects the CHIPS and Science Act will have in the coming years:
- Boost U.S. leadership in semiconductors
- Promote U.S. innovation with wireless supply chains
- Advance the U.S. to be a global leader in technologies for the future
- Boost regional economic growth and development
- Create jobs
- Provide more science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) opportunities to the U.S.
- Drive STEM innovation.
Are There Rising Concerns Over the Future of AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used in a wide variety of industries, including banking, retail, commercial, and government applications. Due to the success of AI in these industries, AI is impending in the manufacturing sector and starting industrial automation. While many in the manufacturing industry have very real concerns about AI and automation, there are many benefits:
- Directed automation: AI is capable of doing repetitive tasks, designing production models, raising competence, avoiding human error, building automatic solutions, and more!
- 24/7 production: Unlike humans who work in shifts, AI works 24/7, allowing businesses to expand their production capabilities and meet high demands for customers across the globe.
- Safer work environments: Humans sometimes need to carry out dangerous or laborious work, leading to workplace injuries and human error. When AI carries out the more dangerous or labor-intensive work, the environment will be much safer for human workers.
- Opportunities for humans: When AI takes over repetitive tasks, human workers will get to focus on innovative and complex work, driving innovation and taking businesses to new levels.
The manufacturing industry has always been open to embracing new and innovative technologies, but obviously, workers have concerns about how much of their job will be automated. Currently, AI does not look to be replacing manufacturing workers any time soon and is on pace to create new opportunities for human workers, focusing on innovative work that will grow their business and the manufacturing industry as a whole. In fact, AI will boost the economic growth an average of 1.7% across 16 industries by 2035, including manufacturing. In addition, by 2035, AI technologies have the impending task to rise in production 40% or more.

Are There Signs Pointing to Sustainable Growth?
According to the Manufacturers Alliance for Productivity and Innovation Foundation, there was a 3.9% growth in production for 2019, with 2.4% growth in 2020 and 1.9% in 2021. This data demonstrates that manufacturing is increasing faster than the general economy. This growth can largely be attributed to an increase in exports and capital growth.
There are other factors spurring growth in the manufacturing industry as well. Here are some more important factors:
- Productivity is increasing
- The domestic production of shale oil and natural gas is growing
- The wages are rising in international markets
- American consumers are supporting American-made products, which supports the American job market
- There is a desire to protect the United States’ intellectual property.
What Does the Manufacturing Industry Need to Thrive?
There are many things the manufacturing industry needs to thrive in the future. For example, the Brookings Institution says government buy-in is essential to propel growth in the manufacturing industry. Other institutions believe open trade policies and access to global markets are key to manufacturing growth.
Either way, avoiding tariff wars and overly restricted trade policies are incredibly important factors to help the manufacturing industry thrive in the future, especially since nearly 50% of U.S. manufactured goods are exported to countries where there are free trade agreements. Brookings Institute also has some more great recommendations to improve the manufacturing environment. Here are some of them.
- Financial incentives: This could include covering education costs, tax credits for equipment expenses, or tax credits for research and development.
- AI: Manufacturers need to embrace AI technologies to keep production and productive quality high.
- Workforce development: Small firms should focus on workforce development and technology research. When this is done, high-paying jobs for skilled workers are created.
- Whistleblower protection: The rules in the industry should encourage transparency and any corruption in the industry should be fought.
- Digital and physical infrastructure: Things like high-speed internet, bridges, roads, and ports need to be invested in to continue supporting efficient manufacturing production.
Pairing Sustainability with Market Expansion
It seems like a different company announces a new plan for sustainability or starts a new advertising campaign every day. Many initiatives focus on helping people and the planet by focusing on improving sustainability of products and processes. When it comes to marketing expansion through sustainability initiatives, there are a few different strategies:
- Fertilizing: In this strategy, the company stays in its existing market and adds a sustainability benefit to their product. This could include changing to organic or natural ingredients or using recycled materials for packaging. In 2018, Carlsberg Brewery launched a new packaging system where glue holds the beer cans together, rather than plastic six-pack rings, which are a hazard to wildlife and a major contributor to ocean pollution. With this sustainability initiative, plastic waste will be reduced by more than 1,000 tons a year after it’s fully rolled out.
- Transplanting: This strategy involves extending sustainability benefits to current products and new ones to adjacent markets. Schneider Electric shifted its focus from traditional electricity-related offerings to energy-efficient offerings. They saw sales more than double over a 15-year period. In addition, Schneider Electric’s stock price quadrupled
- Grafting: This strategy puts the focus on a single sustainability issue with a current product and finds ways to encourage their customers to help address it. A key part of Nike’s sustainability agenda is their commitment to gender equality. Since girls drop out of sports at twice the rate boys do by the age of 14, Nike has invested heavily in in creating quality sports gear for girls and women. Since starting this agenda, Nike’s sales of sports gear for women and girls has grown from 10% of their revenue in the 1990s to over 25% of their revenue today.
- Hybridizing: This strategy is all about brand reinvention with two major shifts: expanding into a new market with a new sustainability initiative and repositioning the brand. The $19 billion Mahindra Group, a leader in agricultural equipment, repositioned their brand with the promise of “creating a nation of champion farmers.” In October of 2022, they introduced Krish-e, a “farming as a service” offering. This was done with the goal of increasing the product yield and income of farmers. With new products and services, Mahindra was able to get farmers to abandon old techniques and embrace a new way of growing crops.

All four of these strategies use a sustainability approach to create value for companies, either by gaining a larger share of their existing market or by entering adjacent markets or creating new ones; there is no one correct strategy. Executives should take the time to identify which strategy is right for their brand.
The future of growth and productivity in the manufacturing industry looks brighter than ever. With the CHIPS and Science Act, sustainability and growth strategies, and everything else that factors into the success of the manufacturing industry taken into consideration, American manufacturing companies can expect to see steady growth and new job opportunities throughout the rest of the decade and beyond.

